[DISPLAY_ULTIMATE_SOCIAL_ICONS]
Surgery
Surgery (from the Greek “hand”, and “work”), via Latin meaning “hand work”) is an ancient medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a patient to investigate and/or treat a pathological condition such as disease or injury, to help improve bodily function or appearance or to repair unwanted ruptured areas (for example, a perforated ear drum).
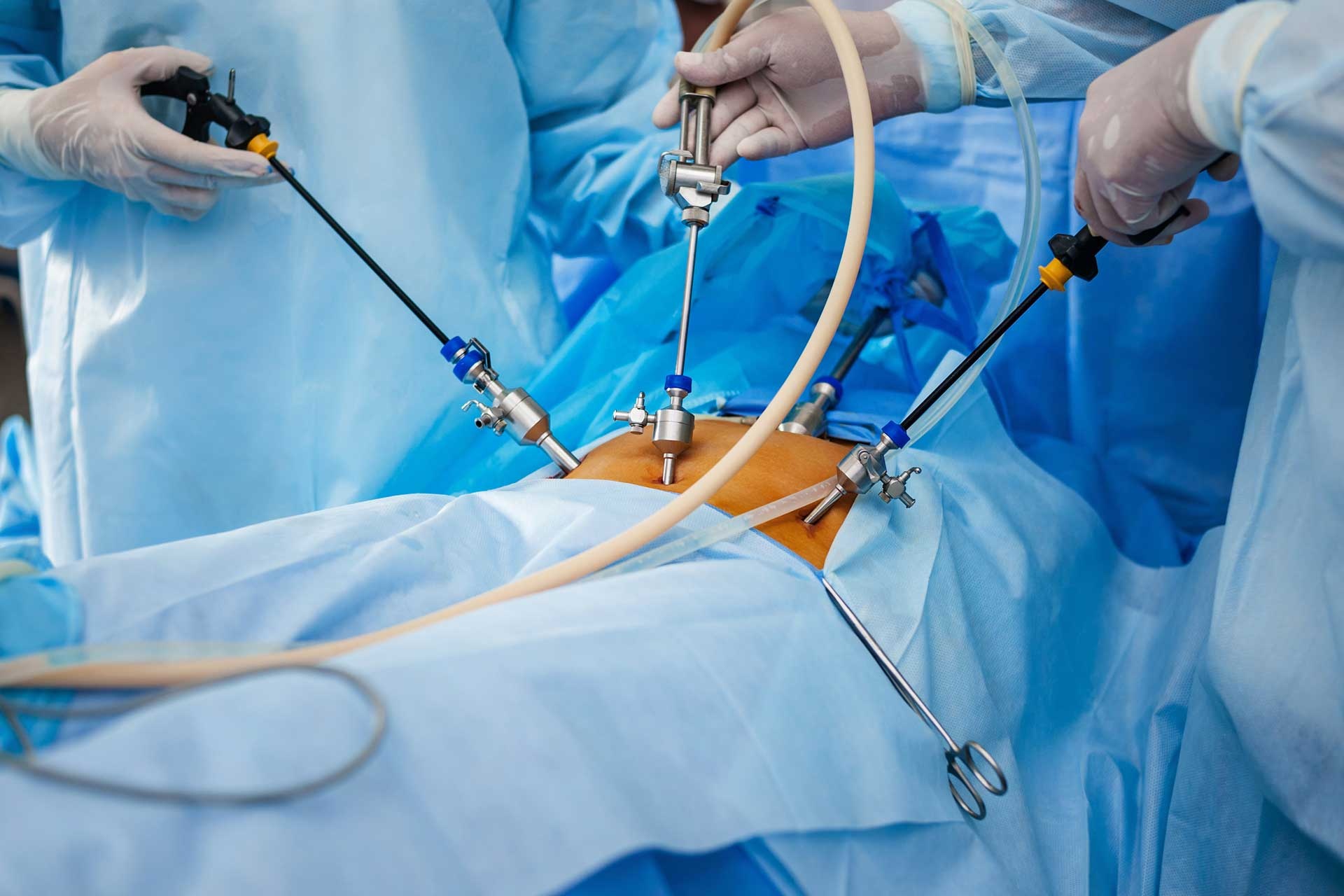
LAPAROSCOPIC SURGERY
- KEYHOLE SURGERY
- MINIMALLY INVASIVE SURGERY (MIS)
- MINIMAL ACCESS SURGERY (MAS)
WHAT OPERATONS CAN WE DO LAPAROSCOPICALLY
Diagnosis
- Crohn’s Disease
- Diverticulitis
- Rectal Prolapse
- Benign renal disease
- Gastric Obstruction
- Some Splenic disorders
- Gallstone
- Appendicitis
- Hernia
- Adhesions
- Perforated ulcer
- Hiatus Hernia
- Colorectal carcinoma
- Caecal carcinoma
- Colonic carcinoma
- Gastric carcinoma
- Oesophageal carcinoma
Operation
- Bowel resection
- Bowel resection
- Repair of Prolapse
- Nephroctomy
- Bypass
- Spleenectomy
- Cholecystectomy
- Appendicectomy
- Hernia repair
- Division of adhesions
- Closure of perforation
- Hiatus hernia repair
- Anterior resection/ APR
- Right Hemicolectomy
- Left/Sigmoid Colectomy
- Gastrectomy
- Oesophagogastrectomy
The list is endless!!!
Principle Differences between Laparoscopic and Open Surgery
FOR THE PATIENT
- Post operative pain related to size of incision- smaller incisions =less pain
- Less Handling of intestines results in little or no disturbance of normal function
- Avoidance of the trauma of abdominal wall injury by the incision allows rapid return to normal activity
- No incision allows early return to more strenuous activities: driving, lifting, sport etc
Principle Differences between laparoscopic and open surgery
For the Surgeon
- Magnified view often better than obtained via an incision allows precise dissection
- Altered (but not absent) tactile response
- Two dimensional (flat screen) view
- Usually (but not always) longer operating time
- Need to develop entirely different operating technique
- Need to develop entirely different operating technique
Some Advanced Laparoscopic Procedures
- Adaptation of principles of open surgery to laparoscopic surgery
- Lap. Cholecystectomy
- Lap. Appendectomy
- Lap. Hiatal hernia repair
- Lap. hernia surgery (groin hernia, ventral hernia, incisional hernia)
- Lap. treatment of heartburn/reflux (Nissen, Toupet fundoplication)
- Lap. treatment of achalasia (Heller myotomy, Dor fundoplication)
- Lap. Bowel resection
- Lap. colorectal surgery (for diverticulitis, cancer, inflammatory bowel disease)
- Lap. stomach surgery
- Lap. splenectomy
- Lap. adrenalectomy
- Lap. lymph node biopsy
- Lap. weight loss surgery
Access and Port Placement
Exploration of CBD
Nissen Fundoplication
Inguinal Hernia Repair
Appendicectomy
Some important procedures
- Appendectomy- An appendectomy is the surgical removal of the appendix, a small tube that branches off the large intestine, to treat acute appendicitis. Appendicitis is the acute inflammation of this tube due to infection.
- Carotid Endarterectomy- Carotid endarterectomy is a surgical procedure to remove blockage from carotid arteries, the arteries located in the neck that supply blood to the brain. Left untreated, a blocked carotid artery can lead to a stroke.
- Cesarean section- Cesarean section (also called a c-section) is the surgical delivery of a baby by an incision through the mother’s abdomen and uterus. This procedure is performed when physicians determine it a safer alternative than a vaginal delivery for the mother, baby, or both.
- Cholecystectomy- A cholecystectomy is surgery to remove the gallbladder (a pear-shaped sac near the right lobe of the liver that holds bile). A gallbladder may need to be removed if the organ is prone to troublesome gallstones, if it is infected, or becomes cancerous.
- Dilation and curettage (Also called D & C.)- A D&C is a minor operation in which the cervix is dilated (expanded) so that the cervical canal and uterine lining can be scraped with a curette (spoon-shaped instrument).
- Hemorrhoidectomy- A hemorrhoidectomy is the surgical removal of hemorrhoids, distended veins in the lower rectum or anus.
- Hysterectomy- A hysterectomy is the surgical removal of a woman’s uterus. This may be performed either through an abdominal incision or vaginally.
- Inguinal hernia repair- Inguinal hernias are protrusions of part of the intestine into the muscles of the groin. Surgical repair pulls the intestine back to its original location.
- Mastectomy- A mastectomy is the removal of all or part of the breast. Mastectomies are usually performed to treat breast cancer.
- Partial colectomy- A partial colectomy is the removal of part of the large intestine (colon) which may be performed to treat cancer of the colon or long-term ulcerative colitis.